Rotary furnace (rotary kiln) smelting working principle framework
1. Main structural components of Rotary furnace
Furnace body: inclined cylindrical structure (refractory lining), can rotate around the axis.
Drive device: motor + gear set, drive the furnace body to rotate at a low speed.
Support wheel: multiple sets of rollers support the furnace body to ensure stable rotation.
Burner: located at the lower end of the furnace body (or a specific position), providing a high-temperature heat source.
Feed port: high-end inlet, materials enter through a screw conveyor/chute.
Discharge port: low-end outlet, materials are discharged after smelting.
Exhaust system: exhaust gas is discharged after dust removal and desulfurization.
Temperature sensor: real-time monitoring of furnace temperature.
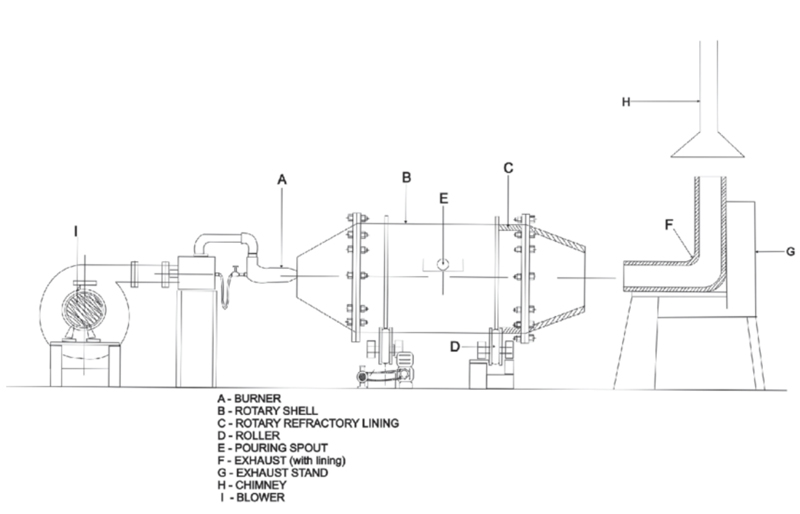
2. Workflow
Feeding: Raw materials (ore, concentrate, etc.) enter the furnace continuously from the high end.
Rotational mixing: The furnace body rotates (0.5~5 RPM), and the materials tumble and slowly move to the low end.
Heating reaction:
The burner sprays fuel (gas/oil/coal powder), and the temperature in the furnace reaches 800~1600℃ (adjusted according to the process).
The material completes reduction/oxidation, sintering or melting reaction at high temperature.
Waste gas treatment: The flue gas generated by the reaction is discharged after dust removal and desulfurization.
Discharging: The smelting product (metal melt/sintered block) is discharged from the low end and enters the next process.
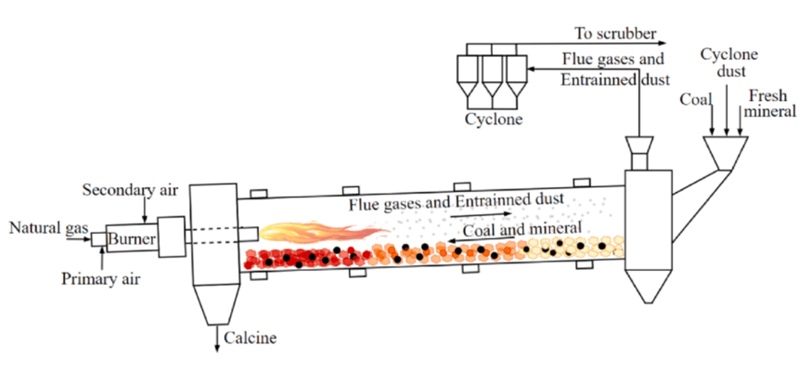
3. Key control parameters
Temperature control: zone temperature control to ensure sufficient reaction.
Tilt angle: 1~5°, control material residence time.
Rotation speed: adjust material mixing efficiency.
Atmosphere control: oxidizing or reducing gas environment.
4. Safety and environmental protection devices
Emergency cooling system: prevent furnace overheating.
Pressure relief valve: avoid abnormal increase of pressure in the furnace.
Waste gas purification device: dust collector + desulfurization tower to reduce pollution.

 Rotary furnace smelting working principle framework-Blog-battery recycling machine,Jiangxi Mingxin
Rotary furnace smelting working principle framework-Blog-battery recycling machine,Jiangxi Mingxin